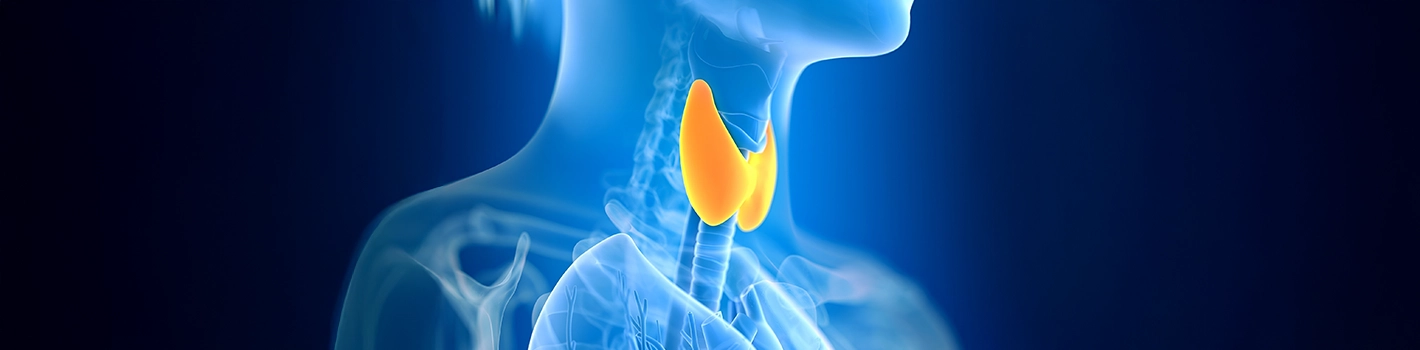
Thyroid and Parathyroid Surgery
The thyroid and parathyroid glands are important glands located in the neck area that regulate the body's metabolism, calcium balance, and hormone production. Thyroid surgery is a procedure that involves the removal of part or all of the thyroid gland due to conditions such as nodules, tumors, or cancer in the thyroid. Parathyroid surgery, on the other hand, is performed to treat disorders of the parathyroid glands, typically conditions like hyperparathyroidism, which disrupt calcium balance in the body.
These are surgical interventions for thyroid gland diseases. They are used to treat conditions such as thyroid nodules, goiter, or cancer. Early diagnosis of the disease results in a higher surgical success rate.
It is a surgical procedure performed in cases of hyperactivity of the parathyroid glands. This procedure helps restore calcium balance in the body and, in the long term, protects bone health.
It is a surgical procedure for the removal of nodules formed in the thyroid gland. This intervention eliminates the risk of nodules turning into cancer and contributes to the regulation of thyroid functions.
It is a surgical procedure that treats excessive hormone production in the parathyroid glands. This helps normalize blood calcium levels and preserves the patient's overall health.
Thyroid Surgery
The thyroid gland is located at the front of the neck and produces hormones that regulate metabolism. Thyroid surgery is typically performed in the following situations:
- Thyroid nodules: Nodules can be benign, but surgery may be necessary in cases where there is a risk of cancer.
- Thyroid cancer: If cancerous cells are detected in the thyroid gland, a part or the entire gland may be removed.
- Goiter: The enlargement of the thyroid gland can lead to symptoms such as swelling in the neck and difficulty breathing; surgical intervention can resolve these issues.
- Hyperthyroidism Excessive production of thyroid hormones can result in symptoms such as palpitations, weight loss, and irritability. When medication is insufficient, surgical treatment may be considered.
Thyroid surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia. During the procedure, a portion of the thyroid gland (lobectomy) or the entire gland (total thyroidectomy) may be removed. After the surgery, the patient is usually monitored in the hospital for a short period and can typically return to normal activities within a few days. In the case of a total thyroidectomy, the patient may need lifelong thyroid hormone replacement.
Parathyroid Surgery
The parathyroid glands are four small glands located behind the thyroid gland, and they regulate calcium balance in the body. Parathyroid surgery is typically performed in cases of hyperparathyroidism. Hyperparathyroidism is a condition where the parathyroid glands produce excessive parathyroid hormone (PTH), leading to elevated calcium levels in the blood. High calcium levels can cause serious health problems in the bones, kidneys, and other organs.
Parathyroid surgery involves the removal of one or more of these glands. Typically, during this surgery, only the overactive glands are removed, and the healthy ones are preserved. After the surgery, calcium levels quickly return to normal, and the patient's symptoms decrease. The surgery can be performed using minimally invasive techniques, though in some cases, larger incisions may be required. Following the surgery, patients generally experience a rapid recovery process.
Thyroid and parathyroid surgery are effective methods for treating diseases of the thyroid and parathyroid glands. Both surgeries should be carefully planned and performed by specialized surgeons. After surgery, patients may need to be regularly monitored by their doctor and may require hormone therapy if necessary. If you are experiencing issues with your thyroid or parathyroid glands, it is important to consult a specialist to determine whether surgical intervention is needed.